ELECTROMYOGRAPHY (EMG)
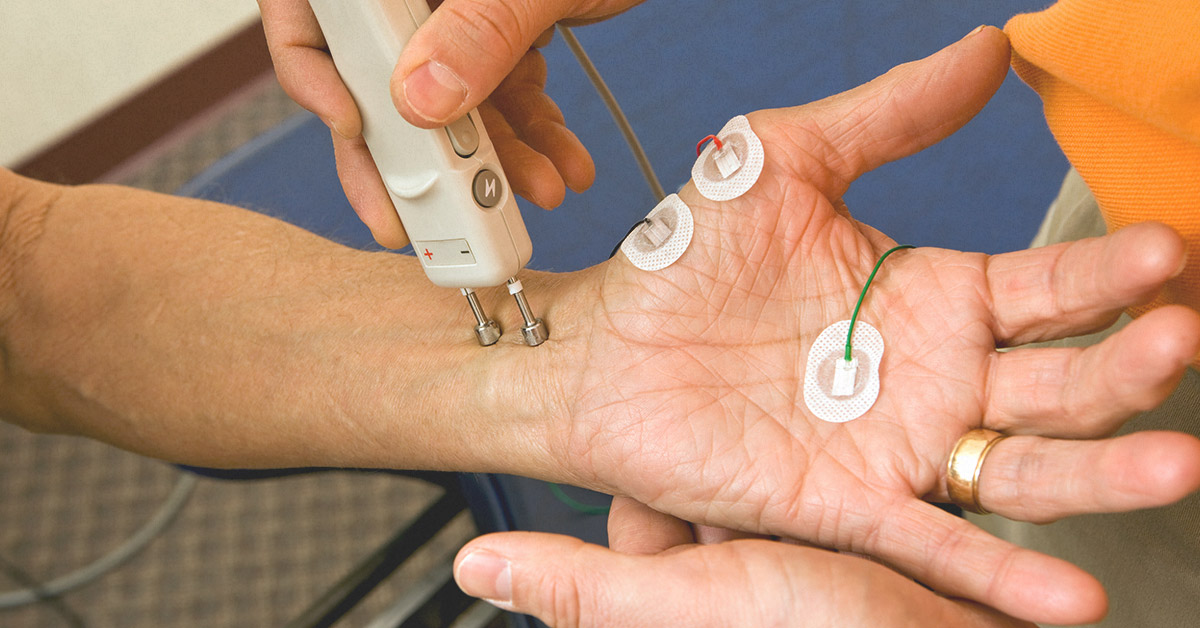
- graphic recording of electrical activity of a muscle at rest and action
- using electromyograph and recorded to electromyogram
- detect the electrical potential generated by muscle cell when these cells contract and at rest
Normal muscle
- at rest shows no electrical activity – voluntary contracture – action potential develops in motor unit
- single motor unit potential – weak contraction
- strong contraction – number of motor units fire simultaneously – superimposed to give – interference pattern
Denervated muscle
- spontaneous electrical activity at rest – denervated potential
- after 15-20 days of muscle denervation
Types of EMG needles used
- concentric
- monopolar
- single fiber
- macro electrode
Three types of activity recorded in EMG
- Insertional activity
- brief action potential – only few seconds – stops immediately when needle movement stops
- decreased in fibrosis or fat tissue replacement
- prolonged in early denervation (irritability), myotonic disorders
- Spontaneous activity
- monophasic (end plate noise) or biphasic ( end plate spikes)
- when needle near a motor end plate
- very short duration
- Voluntary activity
- action potentials from Type I muscle fibers followed by strong ones from Type II fibers
- interference pattern
- prolonged in myopathy
- shortened in neuropathy
Indications
- peripheral neuropathy evaluation
- identifying predominant pathophysiology : axonal/ demylinating, sensory/ motor, acute/sub acute/chronic
- localizing level of lesion ( myelopathic, neuropathic, myopathic)
- objective and qualitative measure of nerve function
Normal results
- muscles at rest – electrically inactive
- after the electrical activity of needle insertion – no abnormal spontaneous activity detected
- voluntary contraction – action potential begin to develop
- strength of contraction increases – more and more fibers produce action potentials
- fully contracted – disorderly group of action potentials of varying rates and amplitudes
Neuropraxia
- normal insertional activity – silent rest activity – no biphasic or triphasic potentials – not interference
Axonotmesis / Neuronotmesis
- increased insertional activity – fibrillation and positive sharp waves in rest – no biphasic, triphasic, interference potentials
Demyelinating neuropathy
- normal insertional and silent rest activity – no bi and triphasic – incomplete interference potential
Contraindications
- abnormal clotting factors, anticoagulant therapy
- extreme swelling
- dermatitis, blood transmittable disorders
- recent MI, pacemakers
Orthopaedics made simple for DNB MS MRCS Support and Guidance for DNB Orthopaedics, MS Orthopaedics and Orthopaedic Surgeons. DNB Ortho MS Ortho MRCS Exam Guide Diplomate of National Board.Our site has been helping dnb ortho post graduates since a long time.It has been providing the dnb ortho theory question papers,dnb orthopedics solved question bank, davangere orthopaedic notes, sion orthopedic notes.We provide guidance to post graduates as to how to pass dnb and ms ortho exams, and aspiring orthopaedic surgeons surgical technique teaching videos and orthopaedic books and pdf.
Get updates email orthoguidance@gmail.com whatsapp 9087747888
- Study Material to Pass Any Orthopaedics Exam
- Davangere Orthopaedic notes pdf
- Dawangere Ortho Notes Hard copy all volumes 2017 edition
- DNB Solved Question Bank with Answers
- Ortho Theory Exam Package
- Ortho Practical exam package
- Ortho case presentation videos
- Orthopaedic Journals
- Orthopaedic Physical Examination video Atlas
- Sion Hospital Orthopaedic Notes
- Orthopaedics Proformas and scheme of practical examination
- Orthopaedic instruments videos and extras
- Video Atlas of Human Anatomy
- Ortho Practical Exam Guide
- MRCS Package
- Orthopaedic Surgery Technique teaching videos - Trauma
- Orthopaedic Surgery Technique teaching videos - Arthroplasty
- Orthopaedic Surgery Technique teaching videos - Spine
- Orthopaedic Surgery Technique teaching videos - Shoulder Arthroscopy
- Orthopaedic Surgery Technique teaching videos - Knee Arthroscopy
- Anatomical Approach technique and exposure teaching videos
- Orthopaedic PG Course Videos










No comments:
Post a Comment